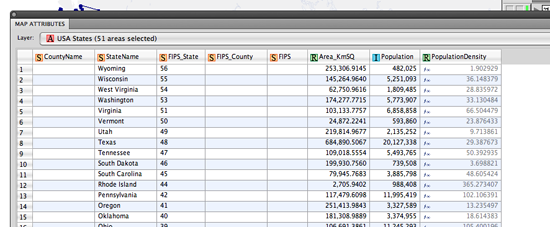
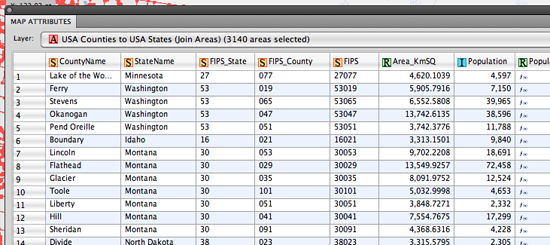
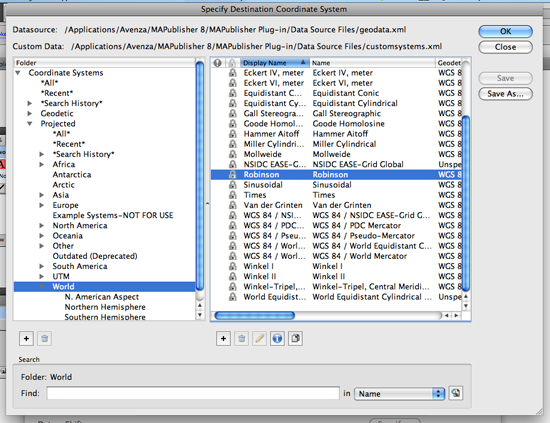
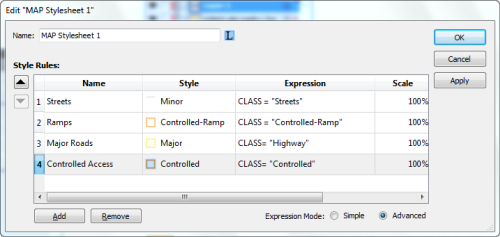
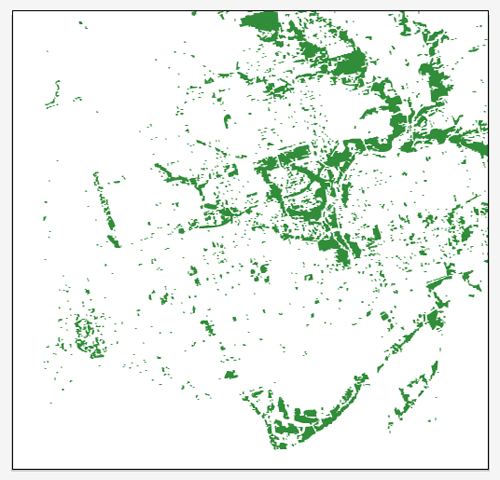
In our previous blog, we introduced you to a quick technique for remote sensing imagery: to depict a type of land types (green area) from a Landsat image. Below is the false composite image created in the previous blog. Basically, the red area indicates a lot of green vegetation (i.e. trees, shrubs, etc).
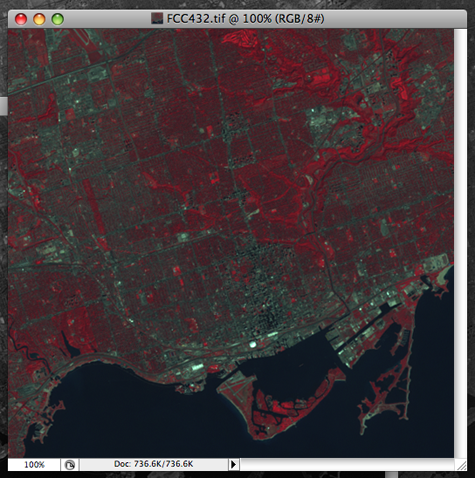
Now, you may be wondering how those red areas can be extracted from Adobe Photoshop and Geographic Imager and brought into Adobe Illustrator and MAPublisher?
An overview of the steps involved in this technique:
In Adobe Photoshop & Geographic Imager:
- Select the red areas with Adobe Photoshop tools.
- Save the selected pixel areas as “work path”.
- Export the saved work path as an Adobe Illustrator file.
- Export the georeference information from Geographic Imager option menu.
In Adobe Illustrator & MAPublisher:
- Import the exported Adobe Illustrator file with the work path.
- Assign the georeference information to the imported work path objects.
- If you have already made a map with vector dataset, open the AI file.
- Import MAP Objects from the AI file with the workpath to another AI file with a map.
- Drag and Drop transformation to align the workpath objects geospatially.
Below are the detailed step-by-step intructions.
In Adobe Photoshop and Geographic Imager:
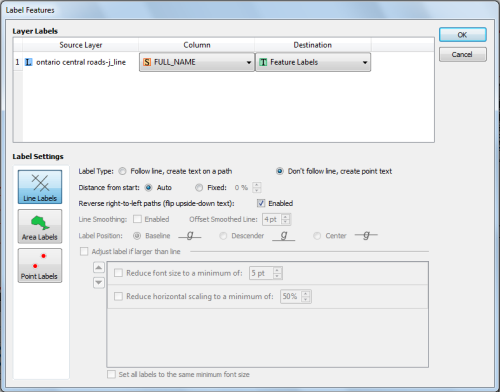
1. Select the red areas
Open the false color composite image in Adobe Photoshop. Now, all the red areas must be selected using any of the following Adobe Photoshop tools.
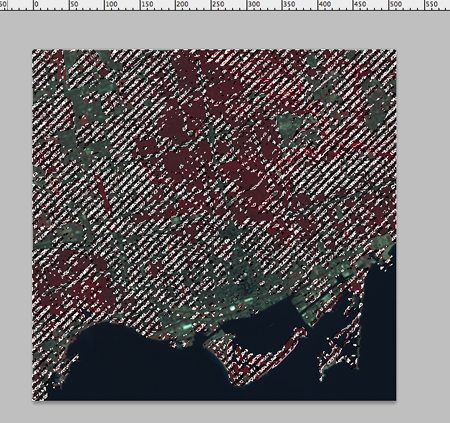
For example, you can select the red areas using the Magic Wand Tool. You may want to adjust the tolerance values as you begin to select the areas so that only the approriate areas are selected. If you disable the “Contiguous” option from the settings tool bar, it selects all the areas with the same color as the one you collected.

If you want to more precisely select red areas with a preview window, use the Color Range Tool (Select > Color Range). With this tool, sample the color of interest first. In this example, you might want to pick only the areas with the bright red color or you might want to be within a specifc range of red. Using this, you will have more control on which areas are selected.
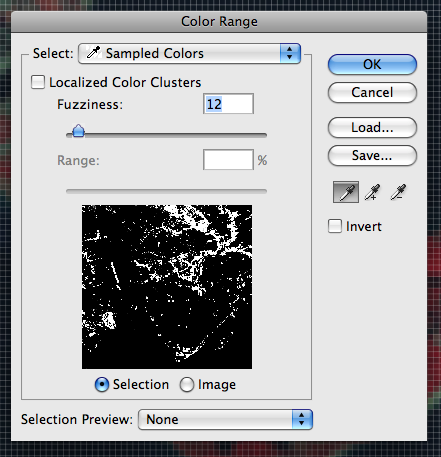
Of course, there are other techniques you can use to collect the pixels with a specific color. The two suggested above are used quite commonly in our workflows.
2. Save the selected pixel areas as “work path”
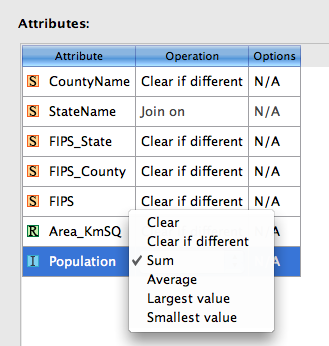
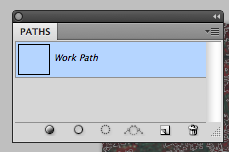
After all the red areas are selected, save the selected area as “work path”. This option is available in the Paths panel options menu.
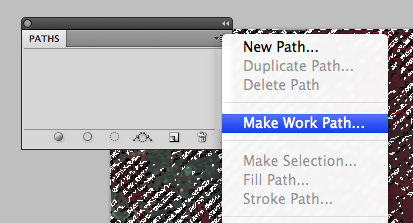
The selection is now saved as a “work path” in the Paths panel.
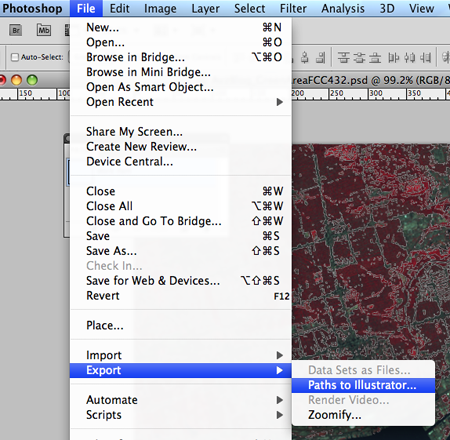
3. Export the saved work path as an Illustrator file
Once the work path is saved in the Paths panel, export it as an Illustrator file (File > Export > Paths to Illustrator).
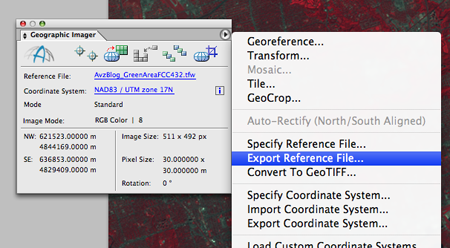
4. Export the georeference information from Geographic Imager option menu
As you saw in the Geographic Imager panel for the false color composite file in the previous blog, this image was georeferenced. Furthermore, we need to export the georeference information that will coincide with the Adobe Illustrator file we just exported.. You can export this georeference information as a MapInfo TAB file or Blue Marble Reference RSF file from the Geographic Imager panel options menu.
In Adobe Illustrator & MAPublisher
5. Import the exported Illustrator file with the work path
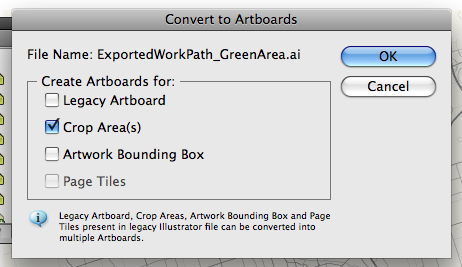
In Adobe Illustrator, open the Adobe Illustrator file exported from Adobe Photoshop (Step 3). Upon opening, a prompt appears to convert the exported file to Artboards. Select the second option “Crop Area(s)”.
When the artboard is opened, it seems like there is nothing on the artboard. It is simply because there is no color assigned to the fill and stroke. I put a green color for the work path objects.
6. Assign the georeference information to the imported work path objects
The imported work path objects do not have the georeference information yet. We exported the reference file in Step 4 using Geographic Imager. We are going to use the exported reference file to assign the georerefernce information to those work path objects.
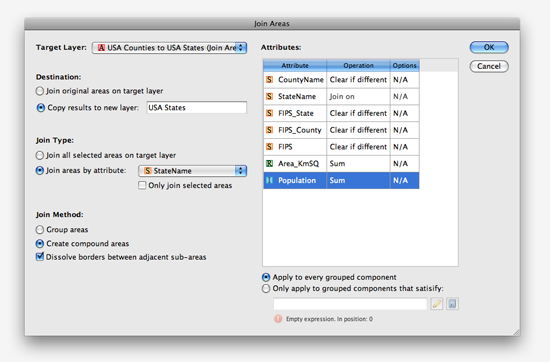
In the MAP Views panel options menu, click “New MAP View For Photoshop Paths…”
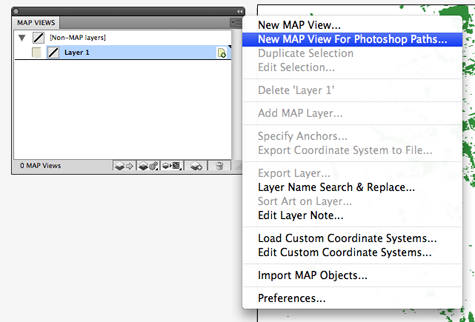
Browse for the exported reference file (either *.tab or *.rsf format from Step 4). Then select “Area” as the feature type for the MAP layer to be created.
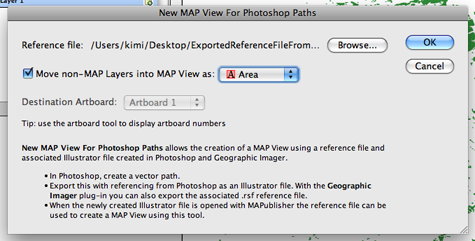
The georeference information from the original image is now inherited by the work path objects in the Adobe Illustrator file.
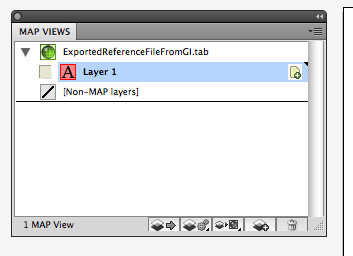
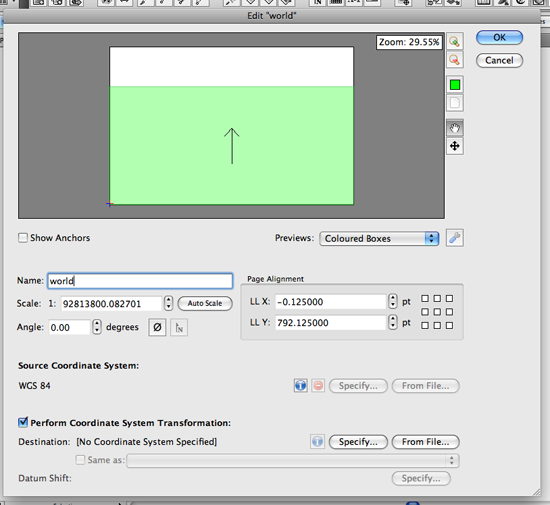
In the MAP View Editor window, you can see all the spatial information such as the coordinate system, scale, and map extent within the artboard. The name for the MAP View is renamed to “Green Area from Photoshop – GI” for Step 8.
At this point, if you have GIS dataset, you can import them to this document. However, I will show you one more MAPublisher trick to bring this green area into an existing MAPublisher file.
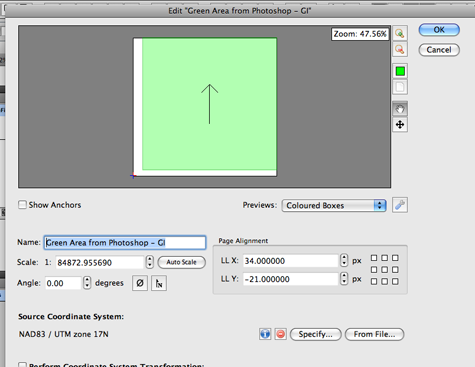
7. If you have already made a map with vector dataset, open the Adobe Illustrator file
Keep the Adobe Illustrator file with the work path objects open, then open another Adobe Illustrator file with MAPublisher MAP Objects. Now you have two Adobe Illustrator documents open.
8. Import MAP Objects from the AI file with the workpath to another AI file with a map
Make the Adobe Illustrator document with the map (not with the work path objects) the current document.
On the MAPublisher Toolbar, click the “Import MAP Object” button.
In the “Import MAP Objects” dialog box, select the MAP View “Green Area from Photoshop” and click OK.
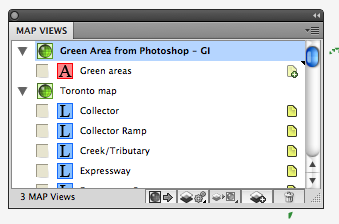
All the path objects are imported to the other Adobe Illustrator file with the base map.
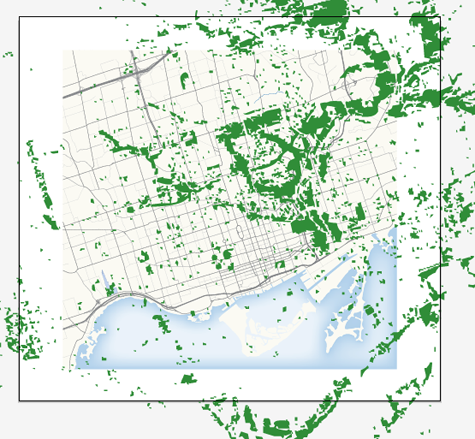
However, the imported objects and the base map do not line up appropriately. It is because the scale of the MAP View with the work path and the MAP View with the base map do not match. You can line up those green areas with a simple step.
9. Drag and drop transformation to align the workpath objects geospatially.
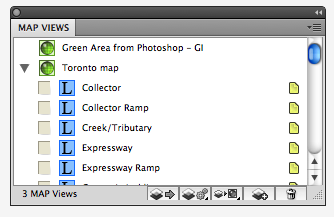
In the MAP Views panel, there are two MAP Views: “Green Area from Photoshop – GI” for the work path imported from another AI file and “Toronto map” for the base map.
Click the MAP Layer “Green areas” in the MAPView “Green Area from Photoshop – GI” …
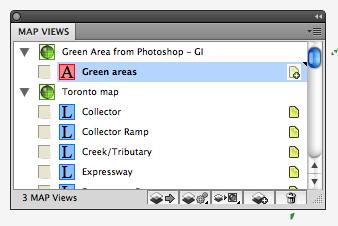
… then drag the map layer to the MAPView “Toronto map”.
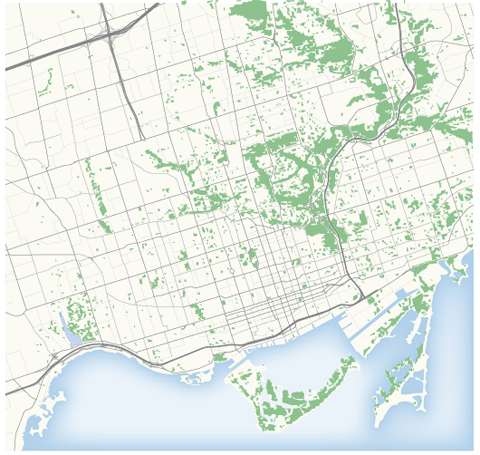
Now all the green areas (work path objects) are lined up nicely with the base map.
Try this out with your own workflow to see how it may improve your maps.