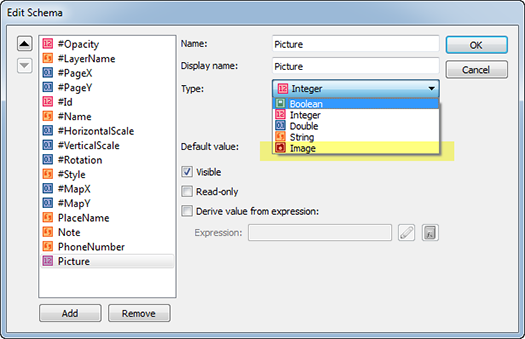
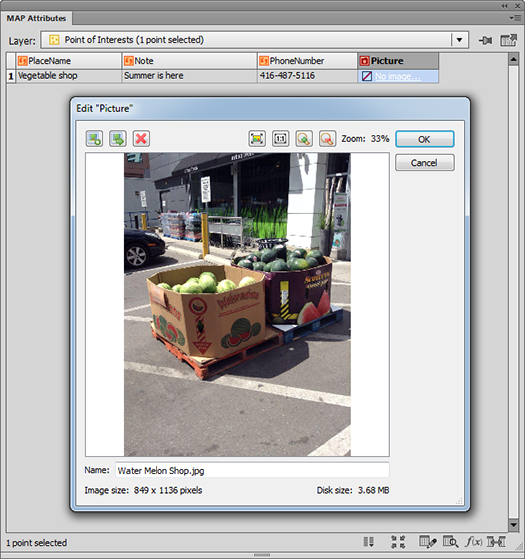
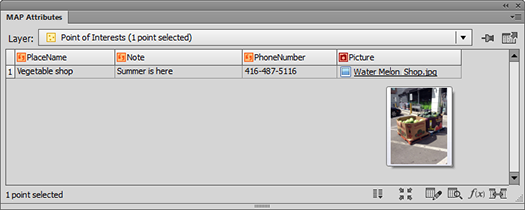
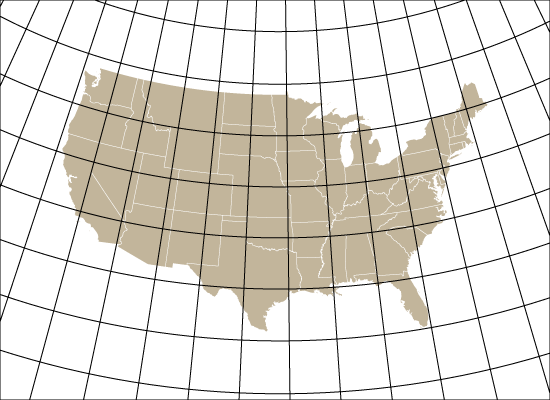
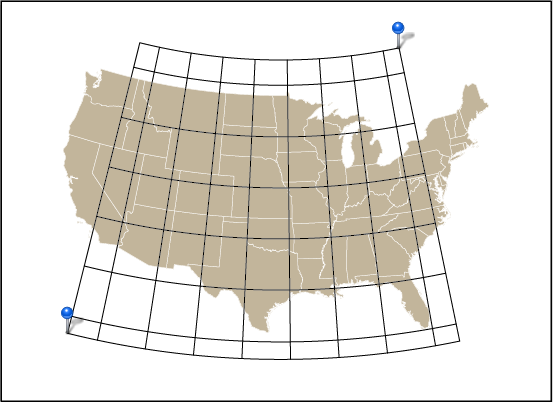
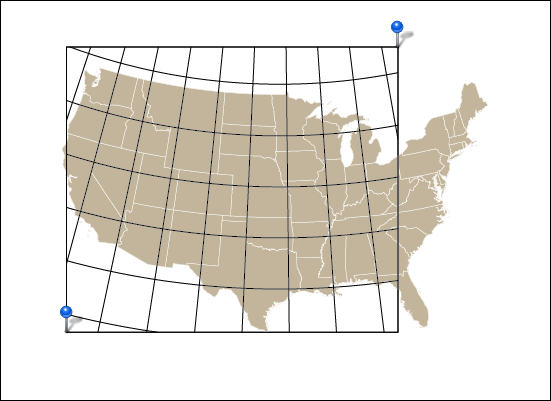
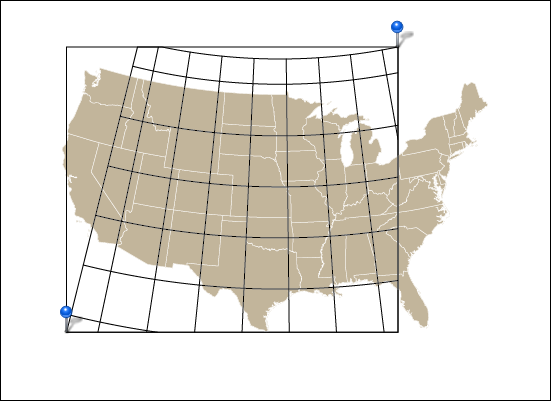
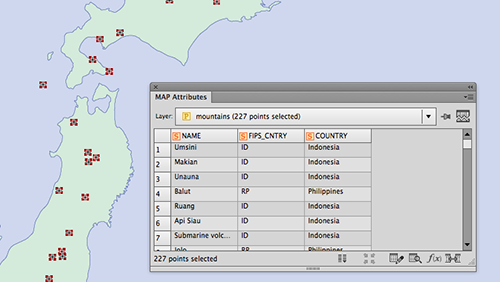
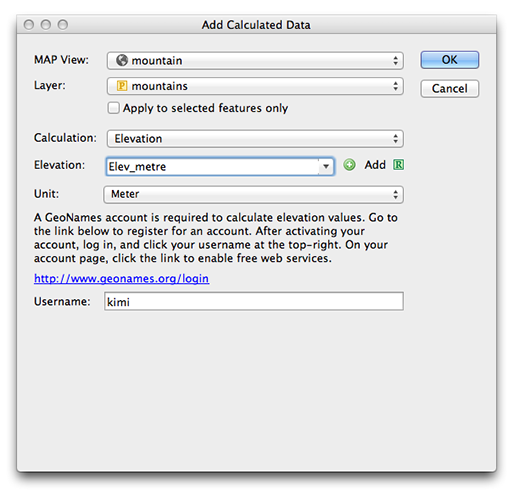
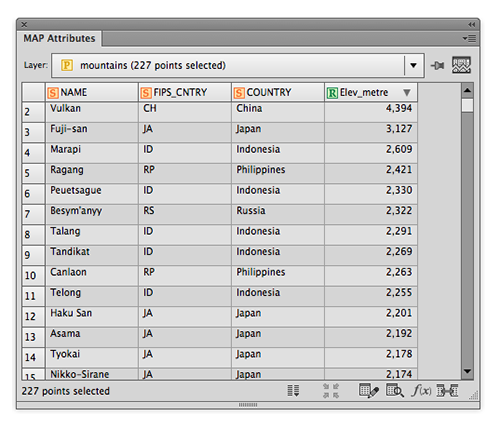
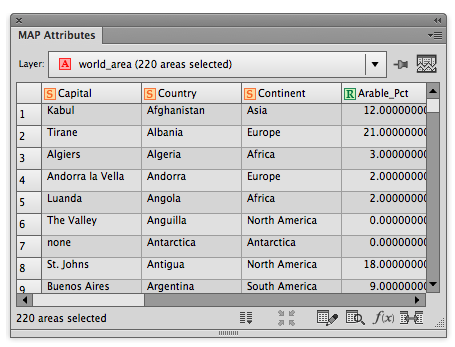
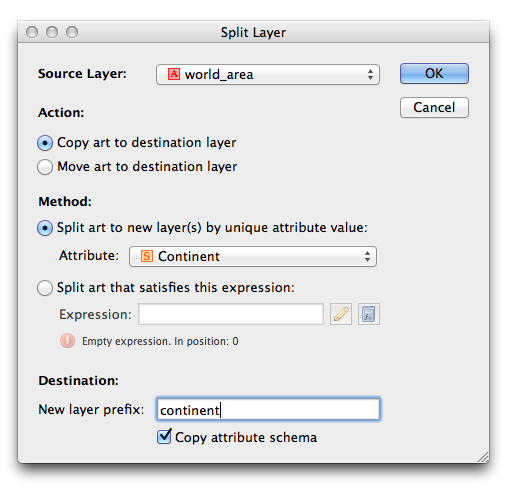
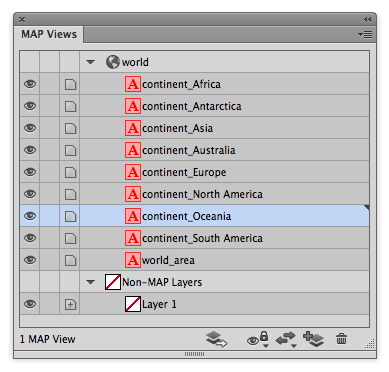
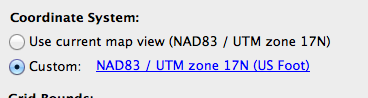
Ever have the problem that you want to make a map and you are waiting on the final extent or scale, but you want to get started adding data and working on the layout? Here are a couple of tips to make your life easier.
1. Move artboards around without moving your data
Geographic features in Adobe Illustrator are generally referenced to a known coordinate system. This coordinate system is mapped to Adobe Illustrator’s “Global Coordinate System” which has its origin at the top-left corner of the first artboard in a document. What this implies is that artboards can be moved around within this reference system in order to show different geographic data on the page. However, by default, moving an artboard moves any art that overlaps it as well. Obviously moving any referenced data around is going to ruin its spatial accuracy so this is something we want to avoid. Luckily there are two ways of doing this.
The first is to select the Artboard tool and click the Move/Copy artwork with artboard button to the right of the artboard name in the control panel above the document window.
With this option turned off, you are free to move the artboard around without disturbing any of the geographic data.
There is one downside to this though: you may have map elements such as titles, legends, grids, masks etc. that you want to stay locked in place on the artboard while you move it around the geographic data. The easiest way to do this is to simply lock any layers that contain geographic features, unlock the map elements, and activate the Move/Copy art with artboard option.

When the artboard is repositioned, your data will stay in the correct geographic location and your map elements will move with the artboard, keeping the same relative position.
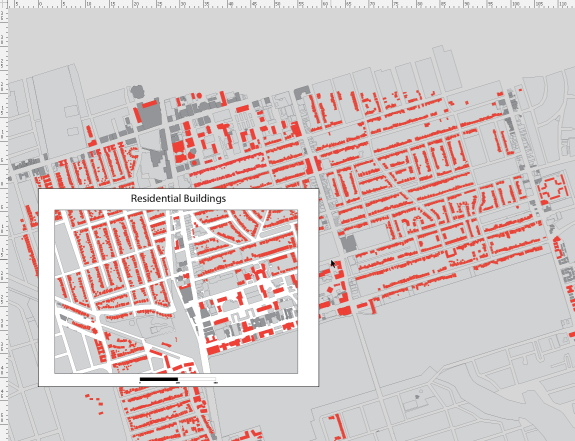
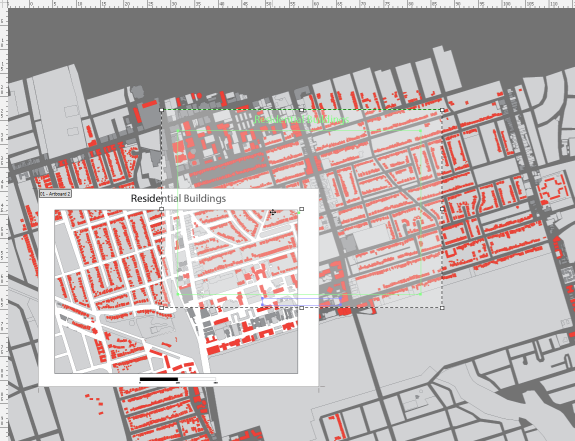
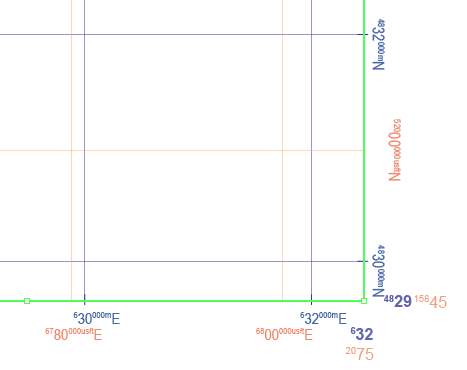
2. Set up a clipping mask in conjunction with a grid
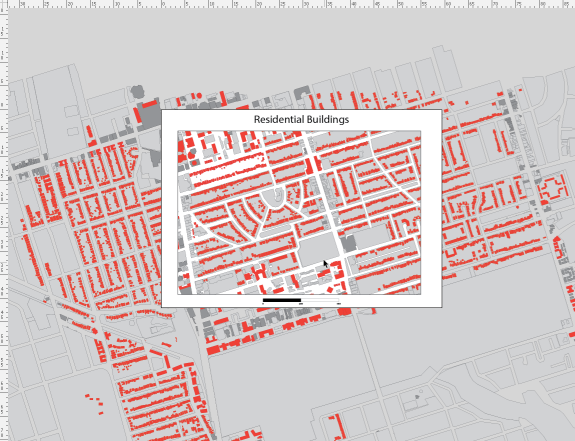
The previous example used a white polygon with a hole in the middle as a mask to provide whitespace around the edge of the map. Another way to achieve this is to use a clipping mask to hide geographic features outside the extent of the mask. This works well by itself, or when combined with a grid or graticule layer.
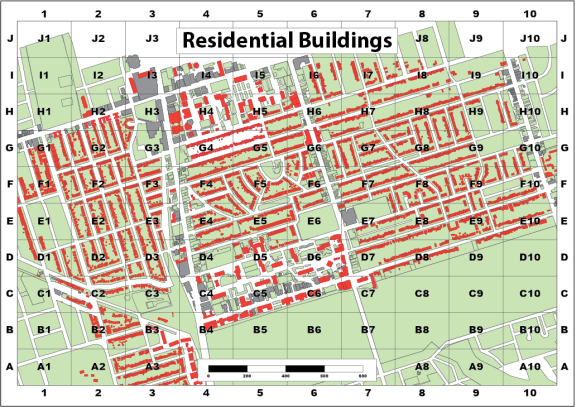
We have taken the previous example, deleted the mask and adjusted the colour of the background polygons slightly. We have also added an AOI polygon that will serve as the clipping mask extent.
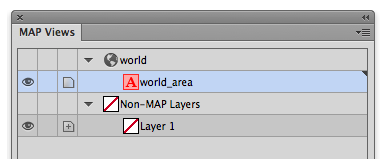
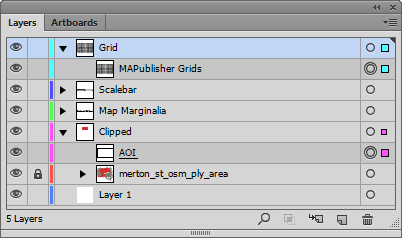
To create a clipping mask, the first thing we’ll make a new layer called Clipped. Make sure that it is a non-MAP layer (verify this in the MAP View panel).
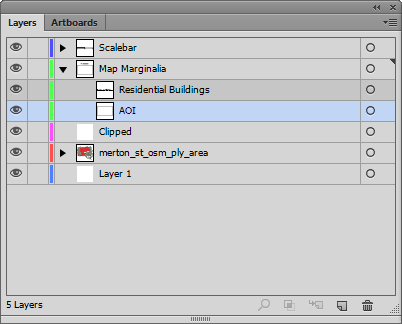
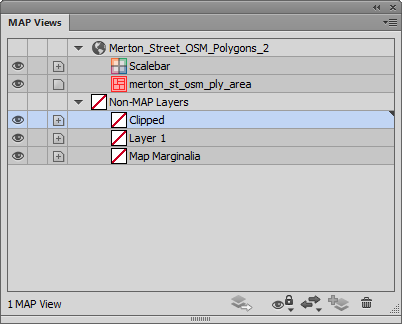
Next, drag both the AOI layer and layers that contain geographic data into the Clipped layer making sure that the AOI rectangle is above the layer holding the geographic features.
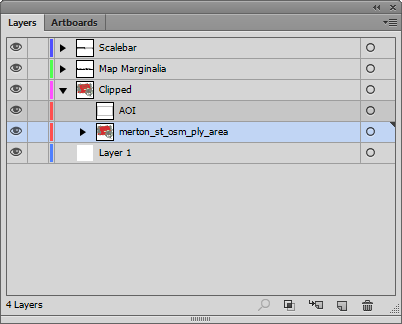
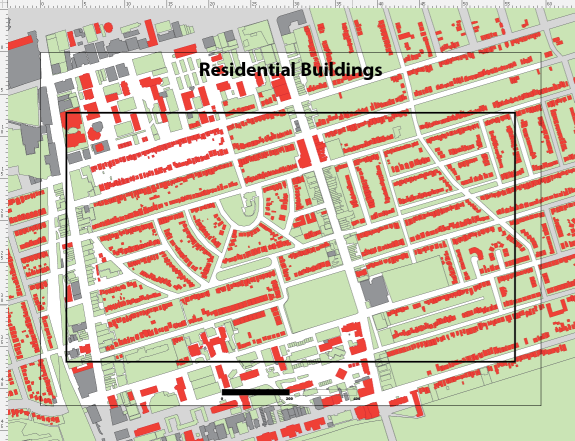
Now if we select the Clipped layer and click on the Make/Release Clipping Mask button (Second from the left at the bottom of the panel) we should see the AOI rectangle become invisible and the MAP layer is visible within the extent of this path.
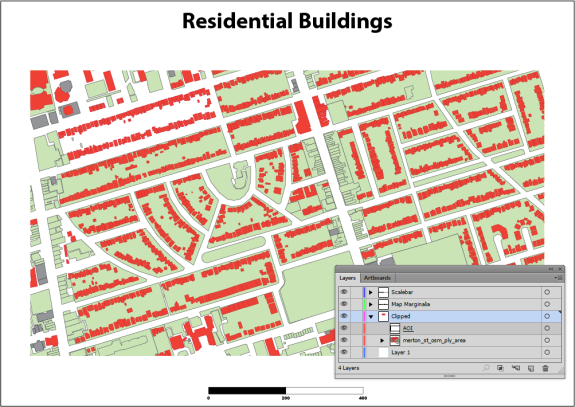
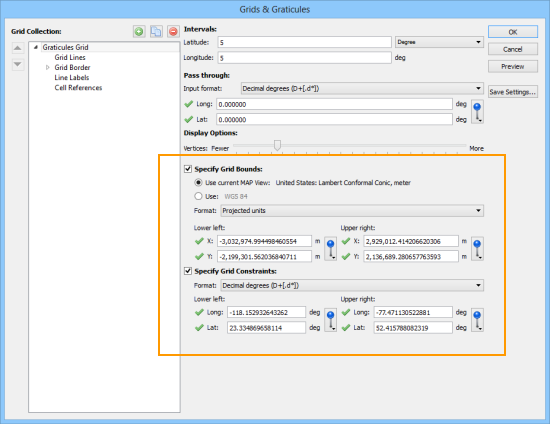
We can now add a grid over the top of the clipped area using the Grids & Graticules tool. You will find that the default extent of the grid is the same as the spatial data. You will need to resize the grid to match the clipping mask.
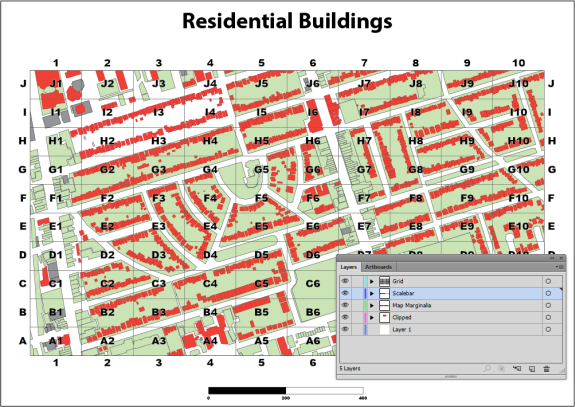
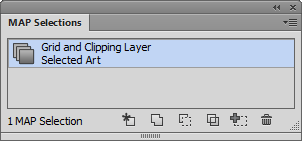
If you want to change the spatial extent of the map you have to adjust both the clipping polygon and the grid. It would be nice to group them and resize it together, but Adobe Illustrator doesn’t allow groups to span multiple layers. One way around this is to use a saved selection. To do this, select the clipping mask and the MAPublisher Grids, then choose Select | Save Selection. Give the selection a name like Grids and Clipping Mask.
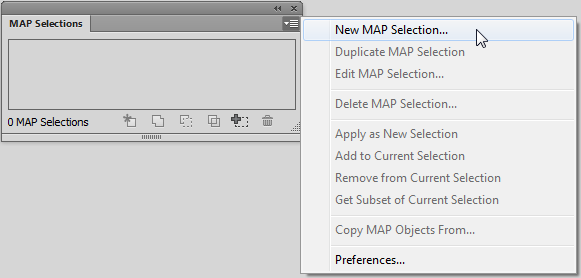
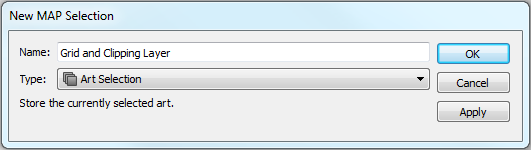
Now if you need to adjust the spatial extent of the map you can quickly choose the saved selection and resize the clipping mask and grid or move them both around the artboard simultaneously.



 We have a CSV file containing points for large cities that we’d like to add to the map. We know from our data source that the CSV uses the WGS84 coordinate system. After selecting the file for import, the MAPublisher Import dialog box helpfully notifies us that some required settings are missing. We’ll click the blue ‘Required settings are missing’ link to continue.
We have a CSV file containing points for large cities that we’d like to add to the map. We know from our data source that the CSV uses the WGS84 coordinate system. After selecting the file for import, the MAPublisher Import dialog box helpfully notifies us that some required settings are missing. We’ll click the blue ‘Required settings are missing’ link to continue.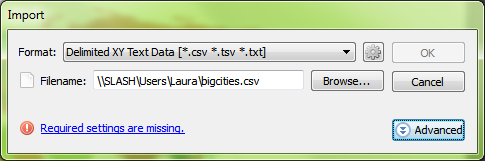 Setting up the import, the coordinate column settings are easy since we have an X_COLUMN and a Y_COLUMN, but we can’t forget to check that the format is correct. The default is Projected units, but we know the file uses WGS84, and can tell by the numbers in the column that the coordinates are in decimal degrees, so we’ll change the format to reflect this information and click OK.
Setting up the import, the coordinate column settings are easy since we have an X_COLUMN and a Y_COLUMN, but we can’t forget to check that the format is correct. The default is Projected units, but we know the file uses WGS84, and can tell by the numbers in the column that the coordinates are in decimal degrees, so we’ll change the format to reflect this information and click OK.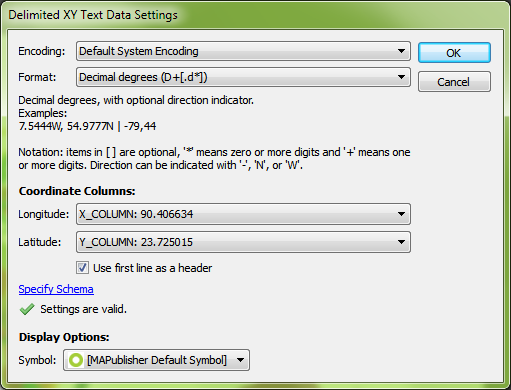 Back at the import window, we see the message ‘Data loaded successfully’. Great! Let’s click OK and add the large cities to the map.
Back at the import window, we see the message ‘Data loaded successfully’. Great! Let’s click OK and add the large cities to the map.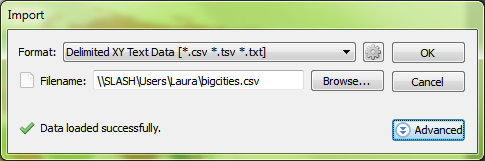 The data has been imported but the result isn’t what we expected. The new layer has been added to a new MAP View, so let’s try dragging it into the Robinson MAP View with the world map.
The data has been imported but the result isn’t what we expected. The new layer has been added to a new MAP View, so let’s try dragging it into the Robinson MAP View with the world map.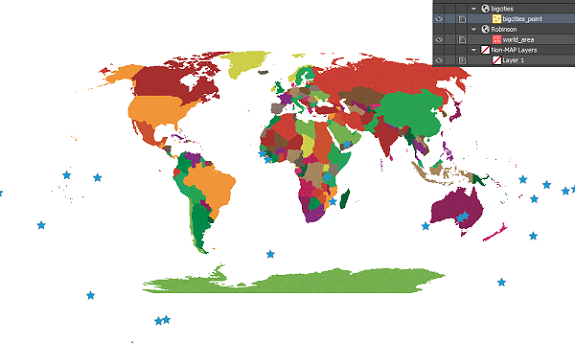 We get a prompt saying that there isn’t any coordinate system information. We want it to be in Robinson like the rest of the map so we’re going to leave the default setting of Same as: Robinson.
We get a prompt saying that there isn’t any coordinate system information. We want it to be in Robinson like the rest of the map so we’re going to leave the default setting of Same as: Robinson.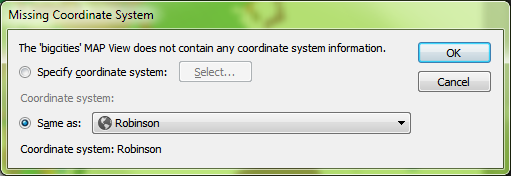 The data has moved, but it still doesn’t look like we were expecting. Where did we go wrong here?
The data has moved, but it still doesn’t look like we were expecting. Where did we go wrong here?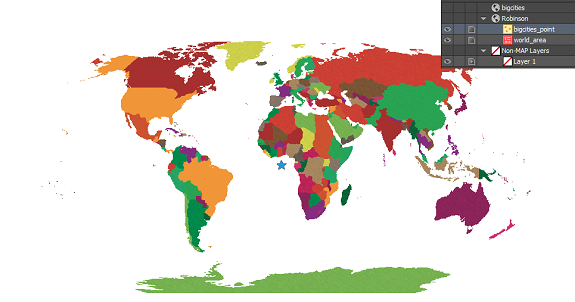 There are actually two places in the workflow where we could have avoided this common mistake. When we dragged the point layer into the Robinson MAP View, the pop-up dialog box prompted that a coordinate system wasn’t specified. We specified Same as: Robinson, thinking this was the correct choice, but we had already determined during import that the CSV was in WGS84. What we should have done here was to specify the coordinate system as WGS84.
There are actually two places in the workflow where we could have avoided this common mistake. When we dragged the point layer into the Robinson MAP View, the pop-up dialog box prompted that a coordinate system wasn’t specified. We specified Same as: Robinson, thinking this was the correct choice, but we had already determined during import that the CSV was in WGS84. What we should have done here was to specify the coordinate system as WGS84.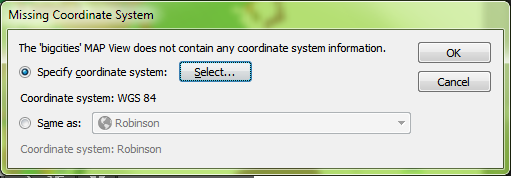 The other place where we could have avoided this error was right after setting up the CSV file for import. In MAPublisher 9.4, there’s a new button on the Import dialog box that allows you to see more detailed information about files being imported. By clicking the Advanced button in the Import dialog box, we would have noticed that there was no coordinate system specified.
The other place where we could have avoided this error was right after setting up the CSV file for import. In MAPublisher 9.4, there’s a new button on the Import dialog box that allows you to see more detailed information about files being imported. By clicking the Advanced button in the Import dialog box, we would have noticed that there was no coordinate system specified.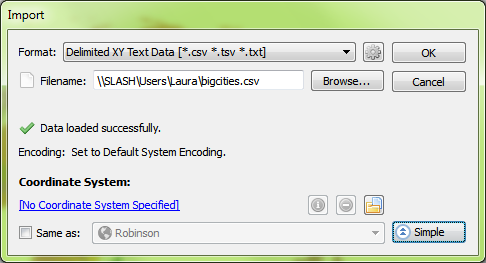 Even here, it might have been tempting to choose Same as: Robinson to add it to the Robinson MAP View, but this would import the points exactly the same as before – all in one location in the middle of the map. Instead, what we want to do is click the blue ‘No Coordinate System Specified’ link and choose WGS84. After this is set up, we’ll click OK to add the data to the map.
Even here, it might have been tempting to choose Same as: Robinson to add it to the Robinson MAP View, but this would import the points exactly the same as before – all in one location in the middle of the map. Instead, what we want to do is click the blue ‘No Coordinate System Specified’ link and choose WGS84. After this is set up, we’ll click OK to add the data to the map.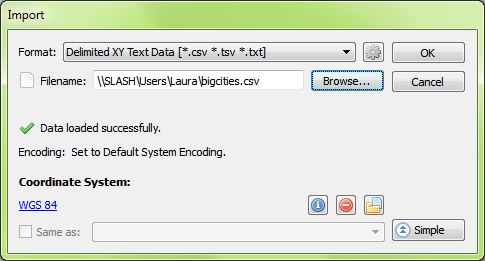 The data still isn’t quite right – it looks the same as when we first imported it. But again we notice that it has been imported into a new MAP View, so we’re going to drag the layer into the Robinson MAP View and see what happens.
The data still isn’t quite right – it looks the same as when we first imported it. But again we notice that it has been imported into a new MAP View, so we’re going to drag the layer into the Robinson MAP View and see what happens.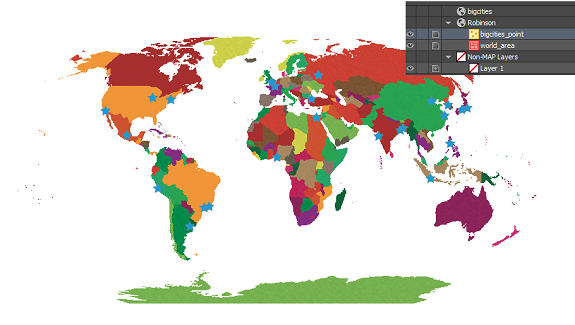 Mistakes during data import are common amongst GIS users, especially those who are just starting out. In the first scenario, when we imported the CSV and added the data directly to the Robinson MAP View, we thought we were telling MAPublisher that we’d like it to match up with the map. What we really did was tell MAPublisher that the data was already in the Robinson projection, even though we knew it was in WGS84. What we should have done first was to define the projection by telling MAPublisher what coordinate system the data is already using. Once MAPublisher knows what system the data is starting in, we can then ask it to project or transform the data into the coordinate system that we’d like to use.
Mistakes during data import are common amongst GIS users, especially those who are just starting out. In the first scenario, when we imported the CSV and added the data directly to the Robinson MAP View, we thought we were telling MAPublisher that we’d like it to match up with the map. What we really did was tell MAPublisher that the data was already in the Robinson projection, even though we knew it was in WGS84. What we should have done first was to define the projection by telling MAPublisher what coordinate system the data is already using. Once MAPublisher knows what system the data is starting in, we can then ask it to project or transform the data into the coordinate system that we’d like to use.