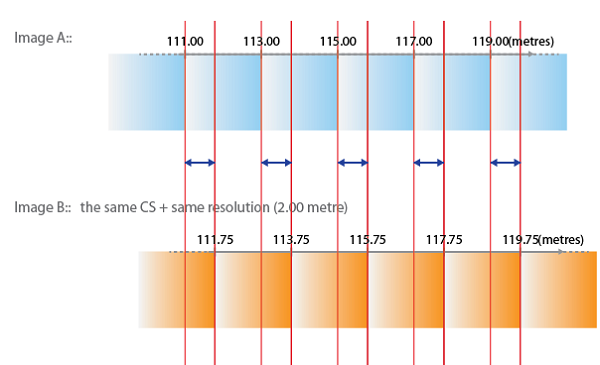
Colorado-based cartographer Mike Boruta knows a thing or two about making maps. In fact, this award-winning cartographer has been designing spectacular maps and trail guides for more than a decade. His work can be seen in the National Geographic Trails Illustrated series, in mountain biking guides released by Fixed Pin Publishing, fly-fishing reference maps curated by Stonefly Press, or most recently in the hiking trails guide for the mountainous town of Ouray, Colorado, where he currently lives. Always fascinated with viewing the world from above, Boruta has dedicated his career to capturing the beauty of mountain landscapes through well-designed maps, and captivating cartographic styles.
Following several years of post-university travel, Boruta found himself living in the tiny tourist-driven town of Ouray. Seeking more opportunities for career advancement, he moved to Arcata, located on the north-western coast of California. He considered returning to school to pursue a computer science degree but realized the subject matter did not entirely excite him. That was when a coworker of his first told him about the excellent Geography and Cartography programs at Humboldt State University nearby. He learned about a subject-stream called Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and although having never heard of GIS before, the concept immediately interested him. His years of travel had given him quite an appreciation for maps, and the GIS and Cartography programs at HSU would allow him to combine this appreciation with an interest in computer technology.
He quickly developed a passion for cartography and decided to pursue graduate schooling in Athens (OH), where he studied under established cartographer Dr. Margaret Pearce. Forever drawn back to the rugged mountain landscapes where he had lived in the past, Boruta found a particular interest in studying relief representation in cartography, the technique used to create the illusion of 3D-terrain on a 2D map. He fell in love with the work of renowned Austrian cartographer Heinrich Berann, whose painterly style “birdseye” mountain maps continue to inspire him today.
“Anytime I had to choose a place to use for projects in my cartography or GIS classes I found myself pulled back West, usually to Ouray, Colorado. I grew increasingly interested in mapping mountainous places”
In 2009, Mike Boruta first began using Avenza MAPublisher in his work. He had recently won the Arthur Robinson Award for Best Printed Map, part of the CaGIS Map Design Competition, for his entry “The Million Dollar Highway”, which explored a scenic stretch of road connecting Ouray to Silverton, Colorado. The award included a student license for Avenza MAPublisher software and allowed him to seamlessly integrate its suite of cartography tools into his already Adobe Illustrator-heavy mapping workflows. Shortly after, he began working with the publishing company Fixed Pin to create a mountain-biking guidebook for the entire state of Colorado. The project was extensive and would require the creation of several complete and detailed map sets, each describing a unique part of the state. Recognizing the vast scale of work ahead of him, Boruta sought out mapping solutions that would help him enhance the efficiency of his cartographic workflow.
“This was the first time I really got to work with MAPublisher, and it was a joy to learn and to use. I immediately found out how useful it was to set up all my graphic styles and character styles since I was having to create 118 maps with the same look and feel.”
As Boruta found himself less and less dependent on dedicated GIS software, he opted to focus on completing his projects from start to finish directly in Adobe Illustrator using the many data import and manipulation tools of MAPublisher. This environment, he felt, “lent itself to so much more creativity”. Integrating these mapping tools into his workflow also meant he did not have to continuously replicate shared design features between each map, instead organizing and stylizing his data into a series of 15 “master maps” and using the MAPublisher Vector Crop tool to create separate individual maps for specific regions.
By 2011, Boruta had begun contract work with National Geographic to help produce maps for the Trails Illustrated line of topographic map products. Incredibly, in 2013 things aligned in such a way that he was able to once again move back to Ouray, the mountain-town he had fallen in love with many years earlier. There, he began meeting with the volunteer-run Ouray Trail Group (OTG) to discuss how he could help them improve their existing trail map, which is a major source of funding for the non-profit group. The first project was getting their map into the Avenza Map Store so that hikers could use the map on their phones and tablets. After that, it was clear that the newly created and extremely popular hiking route called the “Ouray Perimeter Trail” needed its own high-quality map.
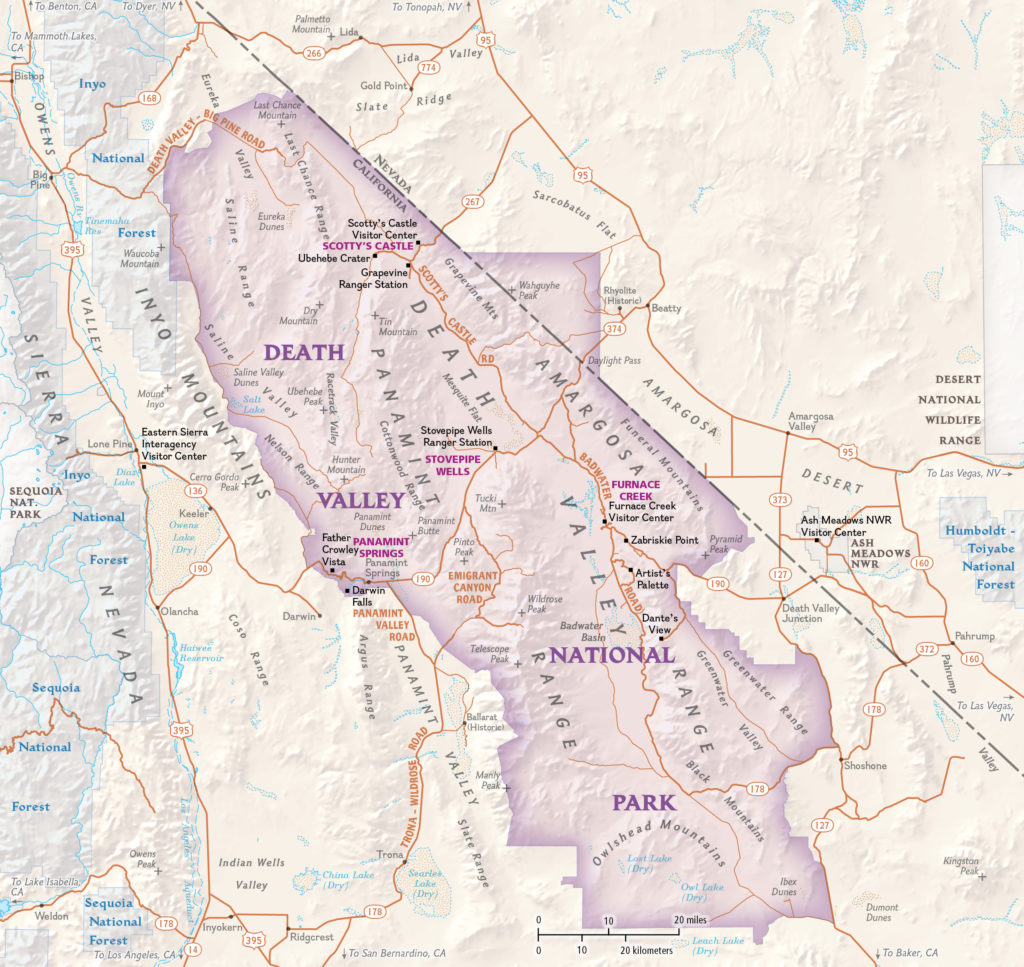
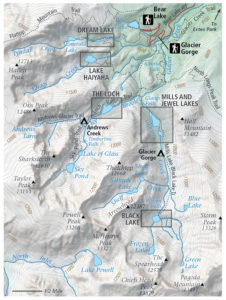
Finding some free time in the summer of 2020, Boruta dedicated himself to fully revising the Ouray Trail Group’s main trail map and also creating an all-new map for the Ouray Perimeter Trail. His vision included a highly-detailed, topographic map showing the entirety of the county’s vast trail system. He set to work collecting datasets and planning the map production, first using dedicated GIS software, before reverting to a more design-focused workflow in Illustrator.
“I quickly moved things into Illustrator and MAPublisher and never looked back. There are certain tasks I’ve grown used to doing in MAPublisher that I just find so much faster and simpler to do than if I were in ArcGIS or QGIS”.
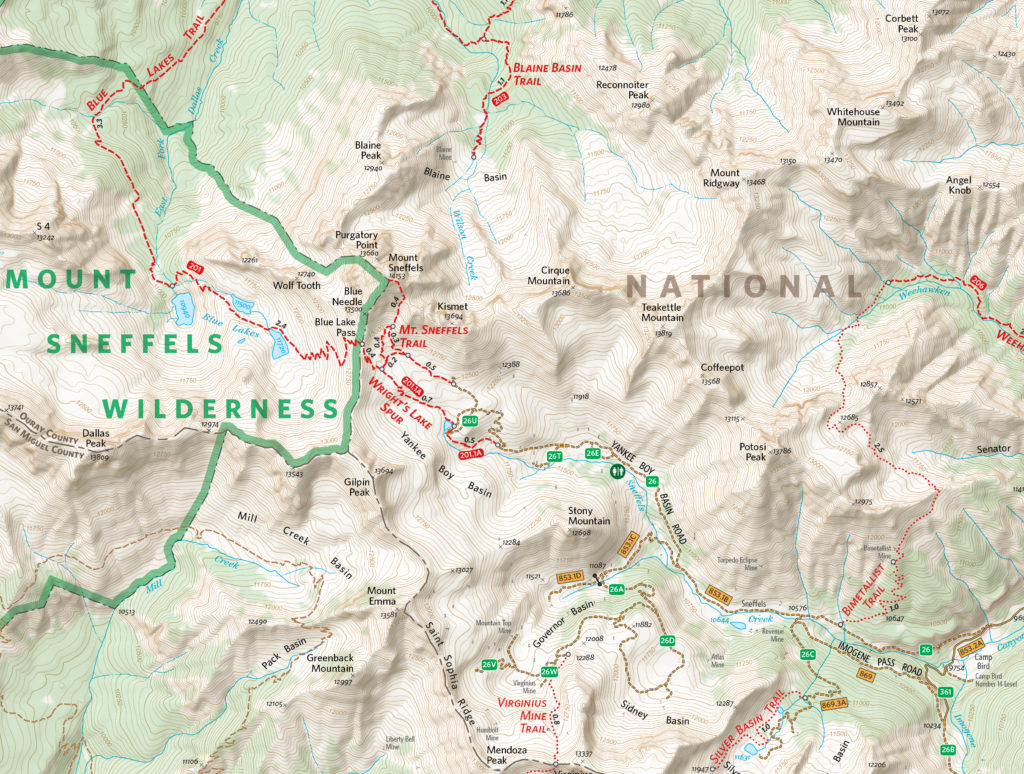
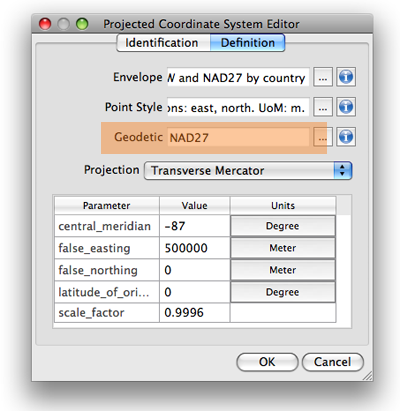
As is common with many mapping workflows, working from mixed data sources can be a constant challenge for many cartographers, especially when data from different public agencies do not share the same projection and coordinate systems. Boruta found this to be a common occurrence while working on his OTG trail maps and highlighted his fondness for being able to drag and drop data into different Map Views directly within Illustrator. In this way, he allowed the software to automatically reproject datasets to a shared projection without having to open up any sort of tool or repeatedly configure data parameters.
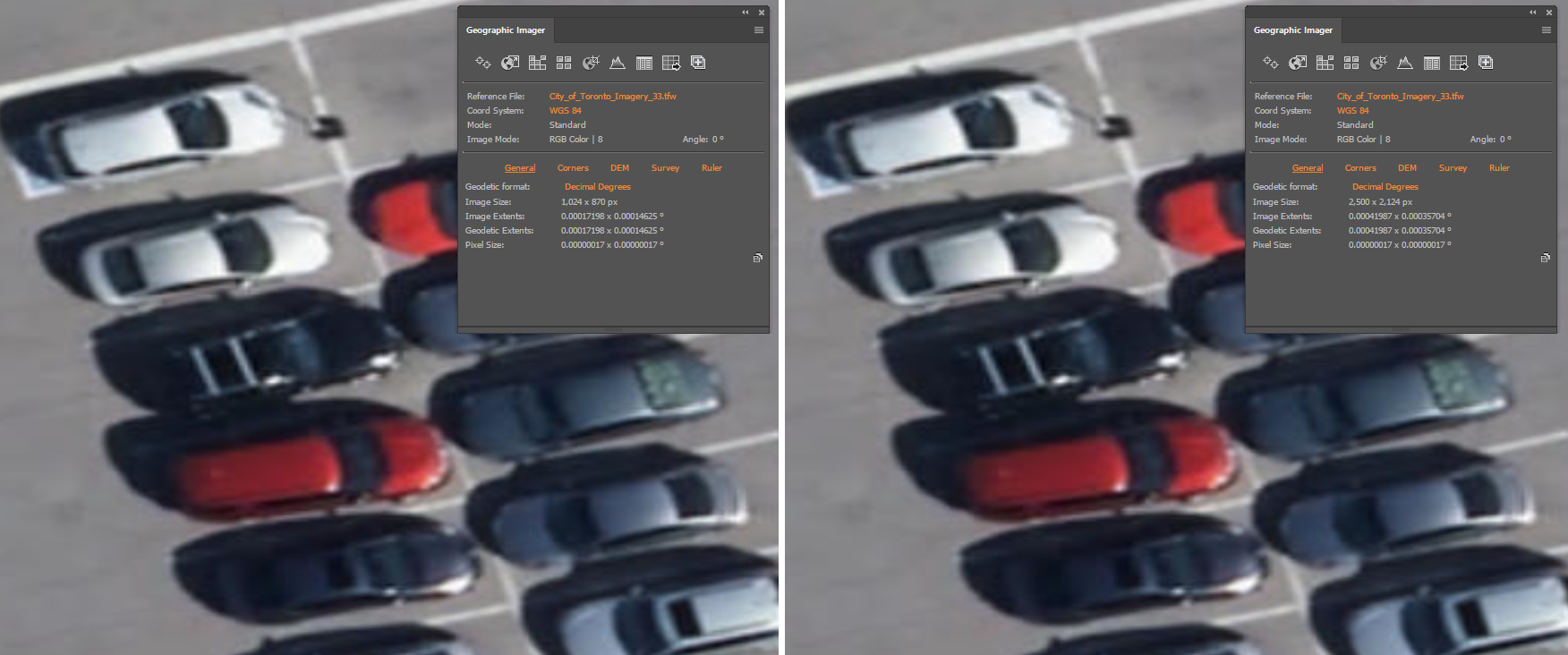
Boruta also emphasized how powerful the Vector Crop tools and “spatial filter on import” capabilities were, allowing him to quickly specify or delineate a region of interest and immediately crop all data layers to that area, retaining topology and attribute integrity, all within the Illustrator environment. When handling the reference maps used to guide the creation of the OTG trail maps, he implemented the Georeferencing tools in the Avenza Geographic Imager plug-in for Adobe Photoshop to efficiently georeference and georectify unprojected reference map images before integrating them back into his Illustrator project. After a large chunk of the summer working on the map, he delivered the finished trail map. On completing the project, he noted “It was one of the most satisfying projects I’ve ever worked on since I was literally mapping my own beloved backyard.”
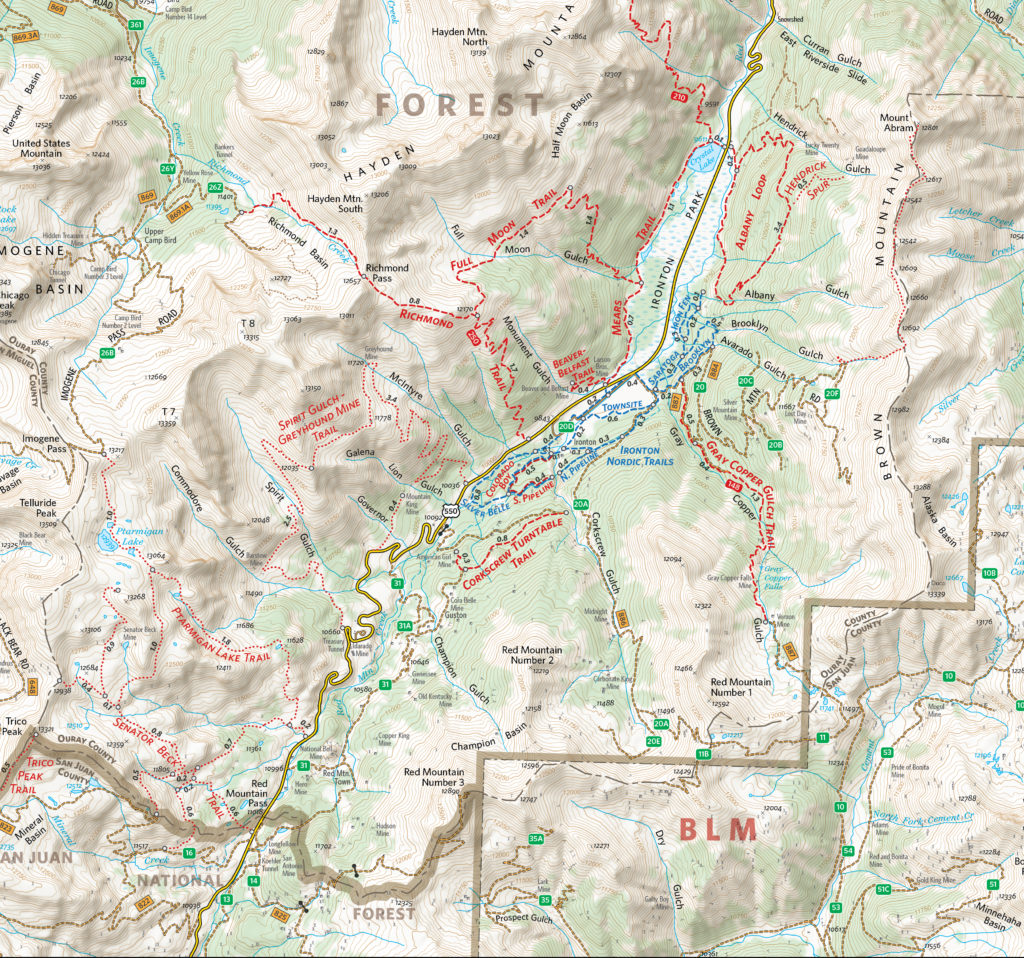
The completed Hiking Trails of Ouray County and the Uncompahgre Wilderness map is available in printed form, and users can also purchase digital forms of that map and the new Ouray Perimeter Trail Map in the Avenza Map Store. The digital maps are fully geo-enabled and support offline use for navigation and GPS-location on mobile devices using the Avenza Maps app.
Mike Boruta still lives in his beloved town of Ouray. He spends his free time enjoying the trails and mountains which he has helped to map. He continues his work for National Geographic and has branched out his interests to include drone photography and videography. He operates the website OuraybyFlight.com, which showcases some of his spectacular drone photography work. His dream is to combine these dramatic landscape panoramas with overlaid symbols and text to create those iconic “birdseye” mountain maps that inspired him years ago.
“I envision something that would hopefully be more aesthetically pleasing, something that aims to capture the soul of these San Juan Mountains while also illustrating the geography. And just maybe it might also be something pretty enough to hang on the wall.”