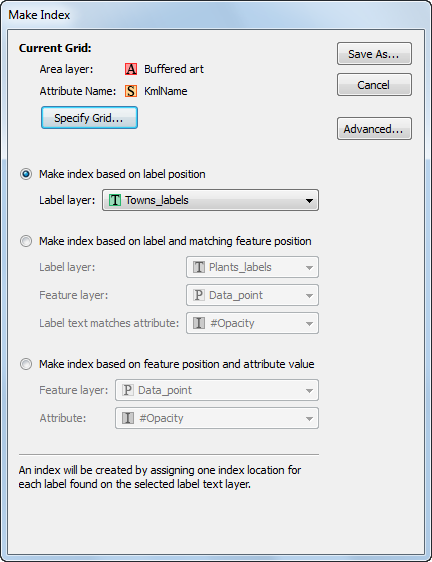
Dot density themes are sometimes called dot distribution maps because they show where particular data characteristics occur. It uses dots or other symbols to represent the number of occurrences of a given data characteristic in a particular location. Starting at MAPublisher 8.4, the ability to create dot density maps is available through the provision of Dot Density Themes.
When creating a new MAP Theme simply choose “Dot Density” from the available theme types. The creation of a dot density theme is facilitated through the MAP Themes panel. The dot density theme is an Adobe Illustrator effect applied to an area layer.
As dot density maps are most useful for showing where particular data occur, they may only be generated for MAP Area type layers. Most often, symbols are used to represent data occurring within a bounding polygon such as a census tract, zip code or county polygons.
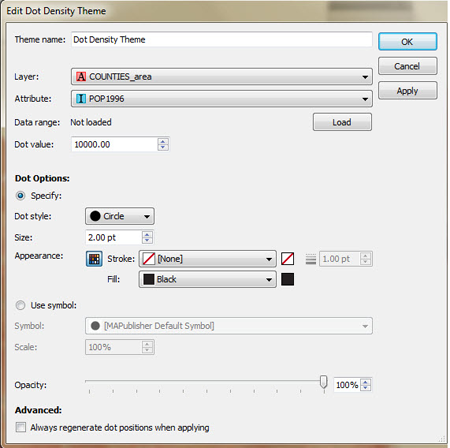
Dot density effects are created on a per layer basis, based on various user defined settings. Data ranges can be determined from selected attribute columns and then a dot value can be assigned a corresponding symbol at which point MAPublisher will map the appropriate results. Users may apply default symbols or load custom ones based on Illustrator symbol sets
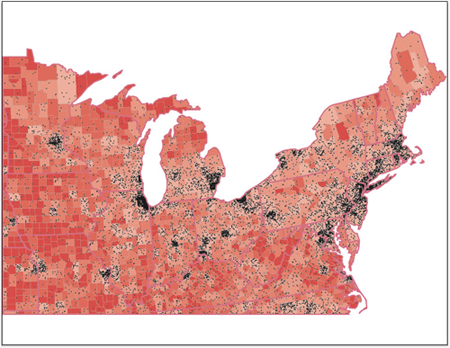
In this example, population tallies per county have been loaded, assigned a dot value of 10,000 with a designated symbol of a 2pt black dot.
This screenshot displays the map prior to applying the dot density effect.
The screenshot below displays the map after having applied the Dot Density Theme using the parameters displayed within the dialog .